Egui First Try 使用Rust开发一个简单的UI
Why
我用Git有一些时间,不过一直是单线git flow,所有的库都是从master/main上拉取,直接在master/main上开发,然后push到远程仓库。因为我的Github Pages是基于Github Actions自动部署的,每次main分支有push,就会自动部署。这个功能一直运行得很好,在前面我写文章的过程中,我一直有一个很不好的感觉,就是commit之后,对推送(附带的Github Actions)有很强的抗拒,总觉得也没给钱而且用了计算时间就相当于排放了二氧化碳。
直到今天,我突然意识到,我可以随便push,只要我checkout到其他分支!这也是为什么Git的分支为什么那么轻,因为Git鼓励多用分支,把所有的工作都正交化。作为一个老年人,我为自己骄傲……我居然还天天都有进步!总之,进步的空间还有很大。
当然我也可能不承认我居然这么笨……我就说我就喜欢用master/main……绝不承认是我没有意识到,用分支工作是git的设计意图。

《The Checklist Manifesto》
这是一本我很喜欢的书,作者是Atul Gawande,他是一位外科医生,也是一位作家。这本书是关于医疗领域的,但是我觉得在软件开发领域,这本书同样适用。

这本书的副标题是:How to Get Things Done That Matter,中文翻译为《清单革命》微信读书。
我马上(大概4个小时)就制定了一个清单,GitHub Pages文章发布清单!
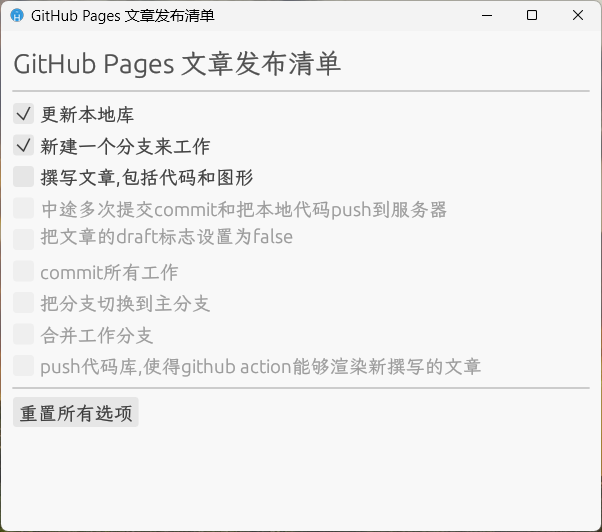
一定每次都更新本地文件,新建分支,……
最重要的是,要把文章的draft改为false,然后再合并分支,推送到远程仓库。
又是不做领域专家的一天
今天根本没有评审、也不需要开会,那当然就是R神启动的一天。
既然需求都那么清楚,当然是编个小程序,顺便看看Rust写界面怎么样。
我倒是在wsl上编译了一个,感觉不太靠谱的样子,回家在Ubuntu上试一下。
总体感觉:
- 单文件发布感觉非常爽;
- 程序的尺寸在合理的范围,就这个没啥功能的玩意,只有5MB多;
- 编写过程非常流畅;
- windows和wsl都能很容易编译,感觉非常棒;
- R神启动,感觉非常爽!
使用Egui
egui是一个将近有2.5万star的Rust> UI库,我也没仔细看,就随便tab,tab,tab一路下来。
有空把代码好好看看,下次一定……下次一定……
UI设计
因为这个需求和内容过于简单,我把主要精力放在了小清新上。
- 使用了小清新开源字体:霞鹜文楷
- 下载字体文件
- 使用了自行设计的清新ICon
- 界面的风格很清新
字体裁剪
因为我们想要的是单一的exe,所以需要裁剪字体。我们用的是pyftsubset,这是一个字体工具,可以用来裁剪字体。编了一个脚本,把我们所需要的字符裁剪出来。
1import os
2import re
3import subprocess
4import sys
5from pathlib import Path
6
7
8def extract_chinese_chars():
9 """从 text.rs 文件中提取所有中文字符"""
10 try:
11 # 获取项目根目录
12 project_root = Path(__file__).parent.parent
13 text_rs_path = project_root / "src" / "text.rs"
14
15 # 读取 text.rs 文件
16 with open(text_rs_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
17 content = f.read()
18
19 # 使用正则表达式提取所有中文字符
20 chinese_chars = re.findall(r'[\u4e00-\u9fff]', content)
21
22 # 去重并排序
23 chinese_chars = sorted(set(chinese_chars))
24
25 # 将字符列表转换为字符串
26 chars_str = "".join(chinese_chars)
27
28 print(f"成功读取 text.rs,提取到 {len(chinese_chars)} 个中文字符")
29 return chars_str
30
31 except Exception as e:
32 print(f"错误:{e}")
33 sys.exit(1)
34
35
36def create_font_subset(chars):
37 """创建字体子集"""
38 project_root = Path(__file__).parent.parent
39 font_path = project_root / "fonts" / "霞鹜文楷.ttf"
40 output_path = project_root / "fonts" / "custom_font.ttf"
41
42 # 检查源字体文件是否存在
43 if not font_path.exists():
44 print(f"错误:字体文件不存在:{font_path}")
45 sys.exit(1)
46
47 print("开始创建字体子集...")
48 try:
49 # 使用 pyftsubset 创建字体子集
50 subprocess.run([
51 "pyftsubset",
52 str(font_path),
53 f"--text={chars}",
54 "--output-file=" + str(output_path),
55 "--no-hinting",
56 "--desubroutinize",
57 "--no-recommended-glyphs",
58 "--layout-features=*",
59 "--glyph-names",
60 "--symbol-cmap",
61 "--legacy-cmap",
62 "--notdef-glyph",
63 "--notdef-outline",
64 "--recommended-glyphs",
65 "--name-IDs=*",
66 "--name-legacy",
67 "--name-languages=*"
68 ], check=True)
69
70 print(f"字体子集创建成功:{output_path}")
71
72 except Exception as e:
73 print(f"创建字体子集失败:{e}")
74 sys.exit(1)
75
76
77def main():
78 print("开始处理...")
79
80 # 提取中文字符
81 chars = extract_chinese_chars()
82
83 # 创建字体子集
84 create_font_subset(chars)
85
86 print("处理完成!")
87
88
89if __name__ == "__main__":
90 main()
为了裁剪方便,我们把程序中的所有文字都放在一个mod中定义:
1pub const WINDOW_TITLE: &str = "GitHub Pages 文章发布清单";
2pub const HEADING: &str = "GitHub Pages 文章发布清单";
3pub const RESET_BUTTON: &str = "重置所有选项";
4
5pub const CHECKLIST_ITEMS: &[&str] = &[
6 "更新本地库",
7 "新建一个分支来工作",
8 "撰写文章,包括代码和图形",
9 "中途多次提交commit和把本地代码push到服务器",
10 "把文章的draft标志设置为false",
11 "commit所有工作",
12 "把分支切换到主分支",
13 "合并工作分支",
14 "push代码库,使得github action能够渲染新撰写的文章",
15];
16
17// 获取所有需要包含在字体中的字符
18// pub fn get_all_chars() -> String {
19// let mut chars = String::new();
20//
21// // 添加标题
22// chars.push_str(WINDOW_TITLE);
23// chars.push_str(HEADING);
24// chars.push_str(RESET_BUTTON);
25//
26// // 添加所有清单项
27// for item in CHECKLIST_ITEMS {
28// chars.push_str(item);
29// }
30//
31// // 去重并排序
32// let mut chars: Vec<char> = chars.chars().collect();
33// chars.sort();
34// chars.dedup();
35//
36// chars.into_iter().collect()
37// }
本来我还想整理一下,就是被注释掉的那点代码,后来感觉没有太大收益就算了。
这个Python基本产生一个文件custom_font.ttf,然后就可以用这个字体了。
在程序中,我们用了一个宏include_bytes!,直接把字体文件嵌入到exe中。
1 fonts.font_data.insert(
2 "custom_font".to_owned(),
3 egui::FontData::from_static(include_bytes!("../fonts/custom_font.ttf")),
4 );
Icon生成
虽然可以在网上下载一个Icon但是,这样不够小清新,我决定用Python生成一个。
1from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
2from pathlib import Path
3import struct
4import io
5
6
7def create_icon_for_size(size):
8 """为特定尺寸创建优化的图标"""
9 # 创建一个新的图像
10 image = Image.new('RGBA', (size, size), (0, 0, 0, 0))
11 draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
12
13 # 计算边距,确保在小尺寸时也有足够的空间
14 margin = max(2, size // 10) # 至少2像素的边距,或者10%的边距
15 circle_bbox = [margin, margin, size - margin, size - margin]
16
17 # 绘制背景圆形
18 draw.ellipse(circle_bbox, fill=(52, 152, 219))
19
20 # 根据尺寸调整字体大小
21 font_size = int(size * 0.6) # 字体占整个图标的60%
22 try:
23 font = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", font_size)
24 except:
25 font = ImageFont.load_default()
26 font_size = int(size * 0.4) # 默认字体需要更小一些
27
28 # 绘制文字 "H"
29 text = "H"
30 text_bbox = draw.textbbox((0, 0), text, font=font)
31 text_width = text_bbox[2] - text_bbox[0]
32 text_height = text_bbox[3] - text_bbox[1]
33
34 # 将H向下移动一点,为波浪号腾出空间
35 x = (size - text_width) // 2
36 y = (size - text_height) // 2 + text_height // 6 # 向下移动一点
37
38 draw.text((x, y), text, fill=(255, 255, 255), font=font)
39
40 # 添加波浪号
41 wave_font_size = int(font_size * 0.5) # 波浪号大小为H的一半
42 try:
43 wave_font = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", wave_font_size)
44 except:
45 wave_font = ImageFont.load_default()
46 wave_font_size = int(size * 0.2)
47
48 wave = "~"
49 wave_bbox = draw.textbbox((0, 0), wave, font=wave_font)
50 wave_width = wave_bbox[2] - wave_bbox[0]
51 wave_height = wave_bbox[3] - wave_bbox[1]
52
53 wave_x = (size - wave_width) // 2
54 wave_y = y - text_height // 2 # 将波浪号放在H上方
55
56 draw.text((wave_x, wave_y), wave, fill=(255, 255, 255), font=wave_font)
57
58 # 对小尺寸图标进行锐化
59 if size <= 32:
60 from PIL import ImageEnhance
61 enhancer = ImageEnhance.Sharpness(image)
62 image = enhancer.enhance(1.5)
63
64 return image
65
66
67def save_ico(images, sizes, output_path):
68 """保存为 ICO 文件"""
69 # ICO 文件头
70 header = struct.pack('<HHH', 0, 1, len(sizes))
71
72 # 目录项
73 directory = b''
74 offset = 6 + len(sizes) * 16 # 6 是文件头大小,16 是每个目录项的大小
75
76 # 图像数据
77 image_data = b''
78
79 for i, (img, size) in enumerate(zip(images, sizes)):
80 # 将图像转换为 PNG 格式
81 png_data = io.BytesIO()
82 img.save(png_data, format='PNG')
83 png_bytes = png_data.getvalue()
84
85 # 计算 PNG 数据大小
86 png_size = len(png_bytes)
87
88 # 如果尺寸大于 255,在目录项中使用 0
89 width = size if size <= 255 else 0
90 height = size if size <= 255 else 0
91
92 # 添加目录项
93 directory += struct.pack('<BBBBHHII',
94 width, # 宽度
95 height, # 高度
96 0, # 颜色数(0 表示 256 色)
97 0, # 保留
98 1, # 颜色平面数
99 32, # 每像素位数
100 png_size, # 图像数据大小
101 offset # 图像数据偏移
102 )
103
104 # 添加图像数据
105 image_data += png_bytes
106 offset += png_size
107
108 # 写入文件
109 with open(output_path, 'wb') as f:
110 f.write(header)
111 f.write(directory)
112 f.write(image_data)
113
114
115def main():
116 print("开始生成图标...")
117
118 # Windows需要的所有图标尺寸
119 sizes = [16, 20, 24, 32, 40, 48, 64, 96, 128, 256, 512]
120 images = []
121
122 # 为每个尺寸创建优化的图标
123 for size in sizes:
124 print(f"生成 {size}x{size} 图标...")
125 image = create_icon_for_size(size)
126 images.append(image)
127
128 # 确保输出目录存在
129 output_dir = Path(__file__).parent.parent / "icons"
130 output_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
131 output_path = output_dir / "app.ico"
132
133 # 保存为ICO文件
134 print("保存ICO文件...")
135 save_ico(images, sizes, output_path)
136
137 print(f"图标文件已生成:{output_path}")
138
139
140if __name__ == "__main__":
141 main()
真的还挺好看的。
主程序
整个程序简直是乏善可陈。
首先是我们的清单,用一个结构体来表示,是一个动态的列表,这里也不涉及到增加,就是在启动的过程中从text.rs中读取。然后就是当前的步骤,用当前的步骤来更新另外一个字段,就是记录当前工作的。这里有一个逻辑:checklist中只能选取勾选当前工作以及之前的选项。如果是当前可选的,那就是完成一项工作,如果是以前已经完成的,就会把所有剩下的工作都标记为未完成。
1struct PostChecklist {
2 steps: Vec<(String, bool)>,
3 current_step: usize, // 当前可操作的步骤
4}
5
6impl Default for PostChecklist {
7 fn default() -> Self {
8 Self {
9 steps: text::CHECKLIST_ITEMS
10 .iter()
11 .map(|&item| (item.to_string(), false))
12 .collect(),
13 current_step: 0,
14 }
15 }
16}
17
18impl PostChecklist {
19 fn update_current_step(&mut self) {
20 // 找到第一个未完成的步骤
21 self.current_step = self
22 .steps
23 .iter()
24 .position(|(_, checked)| !checked)
25 .unwrap_or(self.steps.len());
26 }
27}
主程序的逻辑也很简单,就是为清单结构体实现一个eframe::App,提供一个update函数。
1impl eframe::App for PostChecklist {
2 fn update(&mut self, ctx: &egui::Context, _frame: &mut eframe::Frame) {
3 egui::CentralPanel::default().show(ctx, |ui| {
4 ui.heading(text::HEADING);
5 ui.separator();
6
7 let mut step_changed = false;
8 let mut uncheck_from = None;
9
10 for i in 0..self.steps.len() {
11 let can_check = i <= self.current_step;
12 let step_text = self.steps[i].0.clone();
13 let mut checked = self.steps[i].1;
14
15 if can_check {
16 if ui.checkbox(&mut checked, step_text.as_str()).changed() {
17 self.steps[i].1 = checked;
18 step_changed = true;
19 if !checked {
20 uncheck_from = Some(i + 1);
21 }
22 }
23 } else {
24 ui.add_enabled(false, egui::Checkbox::new(&mut checked, step_text.as_str()));
25 }
26 }
27
28 // 处理状态变化
29 if let Some(from_step) = uncheck_from {
30 for i in from_step..self.steps.len() {
31 self.steps[i].1 = false;
32 }
33 }
34 if step_changed {
35 self.update_current_step();
36 }
37
38 ui.separator();
39 if ui.button(text::RESET_BUTTON).clicked() {
40 for step in &mut self.steps {
41 step.1 = false;
42 }
43 self.current_step = 0;
44 }
45 });
46 }
47}
在这个函数中,就是设置ui的布局和行为,关键的代码在:
1egui::CentralPanel::default().show(ctx, |ui| {
2 ui.heading("GitHub Pages Checklist");
3 ui.separator();
4 ui.checkbox(&mut checklist.steps[checklist.current_step].1, "完成");
5 // ……
6});
这个函数的帮助在:struct CentralPanel.show,最后一个参数用的是一个匿名方法来实现,是要给&mut Ui对象,形参名字为ui。调用Ui所实现的函数,就能完成对UI的更行。这个函数中,我们首先设置了一个标题,然后设置了一个分隔符,然后设置了一个复选框,复选框的值是清单结构体中的当前步骤的完成状态。
相当于是,egui的主线程定时在一定的上下文下调用这个update函数,绘制和更新UI。
主函数中,则主要是设置我们想要的窗口属性,什么一直在最前、窗口尺寸、是否能调整大小……最终调用eframe::run_native来启动程序。
1#![cfg_attr(not(debug_assertions), windows_subsystem = "windows")] // 在 release 模式下使用 windows subsystem
2
3use eframe::egui;
4use egui::IconData;
5mod text;
6
7#[cfg(debug_assertions)]
8fn log(msg: &str) {
9 println!("{}", msg);
10}
11
12#[cfg(not(debug_assertions))]
13fn log(_msg: &str) {}
14
15struct PostChecklist {
16 steps: Vec<(String, bool)>,
17 current_step: usize, // 当前可操作的步骤
18}
19
20impl Default for PostChecklist {
21 fn default() -> Self {
22 Self {
23 steps: text::CHECKLIST_ITEMS
24 .iter()
25 .map(|&item| (item.to_string(), false))
26 .collect(),
27 current_step: 0,
28 }
29 }
30}
31
32impl PostChecklist {
33 fn update_current_step(&mut self) {
34 // 找到第一个未完成的步骤
35 self.current_step = self
36 .steps
37 .iter()
38 .position(|(_, checked)| !checked)
39 .unwrap_or(self.steps.len());
40 }
41
42 // fn uncheck_following_steps(&mut self, from_step: usize) {
43 // // 取消从指定步骤开始的所有后续步骤
44 // for (_, checked) in self.steps.iter_mut().skip(from_step) {
45 // *checked = false;
46 // }
47 // // 更新当前步骤
48 // self.update_current_step();
49 // }
50}
51
52impl eframe::App for PostChecklist {
53 fn update(&mut self, ctx: &egui::Context, _frame: &mut eframe::Frame) {
54 egui::CentralPanel::default().show(ctx, |ui| {
55 ui.heading(text::HEADING);
56 ui.separator();
57
58 let mut step_changed = false;
59 let mut uncheck_from = None;
60
61 for i in 0..self.steps.len() {
62 let can_check = i <= self.current_step;
63 let step_text = self.steps[i].0.clone();
64 let mut checked = self.steps[i].1;
65
66 if can_check {
67 if ui.checkbox(&mut checked, step_text.as_str()).changed() {
68 self.steps[i].1 = checked;
69 step_changed = true;
70 if !checked {
71 uncheck_from = Some(i + 1);
72 }
73 }
74 } else {
75 ui.add_enabled(false, egui::Checkbox::new(&mut checked, step_text.as_str()));
76 }
77 }
78
79 // 处理状态变化
80 if let Some(from_step) = uncheck_from {
81 for i in from_step..self.steps.len() {
82 self.steps[i].1 = false;
83 }
84 }
85 if step_changed {
86 self.update_current_step();
87 }
88
89 ui.separator();
90 if ui.button(text::RESET_BUTTON).clicked() {
91 for step in &mut self.steps {
92 step.1 = false;
93 }
94 self.current_step = 0;
95 }
96 });
97 }
98}
99
100fn main() -> Result<(), eframe::Error> {
101 let options = eframe::NativeOptions {
102 viewport: egui::ViewportBuilder::default()
103 .with_inner_size([600.0, 500.0])
104 .with_resizable(false) // 设置窗口不可调整大小
105 .with_title(text::WINDOW_TITLE)
106 .with_always_on_top()
107 .with_icon(load_icon()),
108 ..Default::default()
109 };
110
111 eframe::run_native(
112 text::WINDOW_TITLE,
113 options,
114 Box::new(|cc| {
115 // 设置中文字体
116 let mut fonts = egui::FontDefinitions::default();
117
118 // 添加自定义字体
119 fonts.font_data.insert(
120 "custom_font".to_owned(),
121 egui::FontData::from_static(include_bytes!("../fonts/custom_font.ttf")),
122 );
123
124 // 将字体添加到所有字体族
125 fonts
126 .families
127 .get_mut(&egui::FontFamily::Proportional)
128 .unwrap()
129 .insert(0, "custom_font".to_owned());
130
131 fonts
132 .families
133 .get_mut(&egui::FontFamily::Monospace)
134 .unwrap()
135 .insert(0, "custom_font".to_owned());
136
137 // 应用字体设置
138 cc.egui_ctx.set_fonts(fonts);
139
140 // 设置界面缩放
141 cc.egui_ctx.set_pixels_per_point(1.5);
142
143 Box::new(PostChecklist::default())
144 }),
145 )
146}
147
148fn load_icon() -> IconData {
149 log("尝试加载嵌入的图标");
150
151 // 嵌入图标文件
152 let icon_bytes = include_bytes!("../icons/app.ico");
153
154 match image::load_from_memory(icon_bytes) {
155 Ok(image) => {
156 log("成功加载嵌入的图标");
157 // 将图像调整为32x32大小,这是Windows图标的标准尺寸
158 let image = image.resize_exact(32, 32, image::imageops::FilterType::Lanczos3);
159 let rgba = image.to_rgba8();
160 let (width, height) = rgba.dimensions();
161 log(&format!("图标尺寸: {}x{}", width, height));
162
163 IconData {
164 rgba: rgba.into_raw(),
165 width: width as _,
166 height: height as _,
167 }
168 }
169 Err(e) => {
170 log(&format!("错误:无法加载嵌入的图标: {}", e));
171 default_icon()
172 }
173 }
174}
175
176fn default_icon() -> IconData {
177 log("使用默认图标");
178 // 创建一个16x16的默认图标,使用蓝色而不是白色
179 let size: u32 = 16;
180 let color = vec![0u8, 102, 204, 255];
181 let mut rgba = Vec::with_capacity((size * size * 4) as usize);
182 for _ in 0..((size * size) as usize) {
183 rgba.extend_from_slice(&color);
184 }
185 IconData {
186 rgba,
187 width: size,
188 height: size,
189 }
190}
Windows打包
这个程序还有一点点复杂的就是windows下打包成Windows subsystem的exe。这里就不涉及技术细节了,我可以不是自己不懂……哈哈哈哈哈
1#[cfg(windows)]
2fn main() {
3 use std::io::Write;
4 let mut res = winres::WindowsResource::new();
5
6 // 设置图标
7 res.set_icon("icons/app.ico");
8
9 // 设置清单文件
10 let manifest = r#"<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
11<assembly xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" manifestVersion="1.0">
12 <trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3">
13 <security>
14 <requestedPrivileges>
15 <requestedExecutionLevel level="asInvoker" uiAccess="false"/>
16 </requestedPrivileges>
17 </security>
18 </trustInfo>
19</assembly>"#;
20
21 let manifest_path = "target/app.manifest";
22 std::fs::create_dir_all("target").unwrap();
23 let mut manifest_file = std::fs::File::create(manifest_path).unwrap();
24 manifest_file.write_all(manifest.as_bytes()).unwrap();
25
26 res.set_manifest_file(manifest_path);
27
28 // 设置应用程序版本信息
29 res.set_version_info(winres::VersionInfo::PRODUCTVERSION, 0x00010000);
30 res.set_version_info(winres::VersionInfo::FILEVERSION, 0x00010000);
31 res.set("ProductName", "Hugo Post Manifesto");
32 res.set("FileDescription", "Hugo Post Manifesto");
33 res.set("LegalCopyright", "Copyright (c) 2024");
34
35 if let Err(e) = res.compile() {
36 eprintln!("Error: {}", e);
37 std::process::exit(1);
38 }
39}
40
41#[cfg(not(windows))]
42fn main() {}
总结
全部工程需要的文件:
这些文件都可以在Github仓库中找到。
文章标签
|-->rust |-->egui |-->checklist |-->github pages |-->rust-lang |-->清单革命 |-->git branch |-->python |-->icon |-->font |-->font-cutter |-->字体裁剪
- 本站总访问量:loading次
- 本站总访客数:loading人
- 可通过邮件联系作者:Email大福
- 也可以访问技术博客:大福是小强
- 也可以在知乎搞抽象:知乎-大福
- Comments, requests, and/or opinions go to: Github Repository
