<-- Home
|--matlab
|--quickanswer
QuickCodeAndResults(1)
results
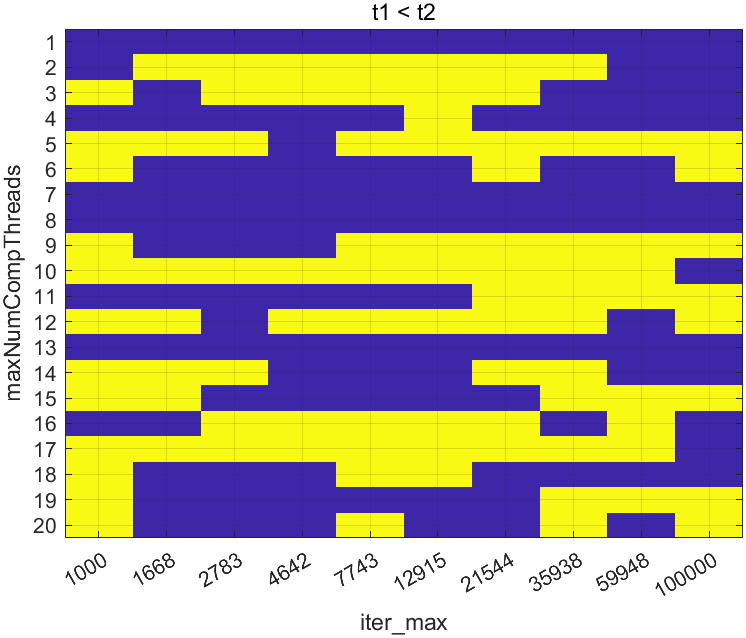
这里的黄色对应与$t_1 < t_2$的情况,即第一个算法的运行时间小于第二个算法的运行时间。
并没有显著的性能差异。
Matlab Code
用于评估的脚本,最好是把timeit的评估对象包装为函数,可以去掉首次调用的时间。
1%% Jacobi iteration
2clear;
3epsilon = 1; a = 1/2; n = 150; h = 1 / n;
4A = tridiag(n, [epsilon; - (2 * epsilon + h); epsilon + h]);
5b = zeros(n, 1);
6b(1:n) = a * h * h;
7x_init = zeros(n, 1);
8
9%% calculation
10for n = 1:20
11 maxNumCompThreads(n);
12 fprintf("maxNumCompThreads = %d\n", maxNumCompThreads);
13 iter_times = round(logspace(3, 5, 10));
14 t1 = arrayfun(@(n)timeit(@()iter_jacobi(A, b, x_init, 1.0e-7, n, 0), 2), iter_times);
15 t2 = arrayfun(@(n)timeit(@()iter_jacobi(A, b, x_init, 1.0e-7, n, 1), 2), iter_times);
16 save(sprintf("comparison-%d", maxNumCompThreads), "t1", "t2");
17 fprintf("i=1:n\t");
18 fprintf("%.8f\t", t1);
19 fprintf("\n");
20 fprintf("i=1:n-1\t");
21 fprintf("%.8f\t", t2);
22 fprintf("\n");
23end
24
25%% visualize
26figure;
27plot(iter_times, t1, 'x-', iter_times, t2, 'o-')
28legend({"i=1:n", "i=1:n-1"}, 'Location', 'best')
29xlabel("iter_max")
30ylabel("Time(s)")
31
32%% maxNumCompThreads x iter_max
33
34% calculate a matrix, row = numel(1:20), column = numel(iter_times)
35% if t1(i, j) < t2(i, j), then 1, else 0
36
37numCompThreads = 1:20;
38iter_times = round(logspace(3, 5, 10));
39comparison = zeros(numel(numCompThreads), numel(iter_times));
40
41for i = 1:numel(numCompThreads)
42 load(sprintf("comparison-%d", i), "t1", "t2");
43 comparison(i, :) = t1 < t2;
44end
45
46figure;
47
48imagesc(comparison, [0, 1])
49xlabel("iter_max", 'Interpreter', 'none')
50xticklabels(iter_times)
51ylabel("maxNumCompThreads")
52yticks(numCompThreads)
53yticklabels(numCompThreads)
54title("t1 < t2")
55grid on
56
57exportgraphics(gca, "yellow_for_t1_le_t2.png")
58
59%% calculate t1 and t2 for default maxNumCompThreads, 1000 times, iter_max = 100000
60maxNumCompThreads('automatic')
61iter_times = 1000;
62t1 = arrayfun(@(~)timeit(@()iter_jacobi(A, b, x_init, 1.0e-7, iter_times, 0), 2), 1:100);
63t2 = arrayfun(@(~)timeit(@()iter_jacobi(A, b, x_init, 1.0e-7, iter_times, 1), 2), 1:100);
64
65% there is no evidence that, t1 is significantly small than t2
66% and the actual calculation is equivalent with i=1:n-1 and i=1:n
67% since: j = i+1:n
待评估的核心代码:
1function [x_iter, iter_times] = iter_jacobi(A, b, x_init, tol, iter_max, flag)
2
3 if nargin < 6
4 flag = 0;
5 end
6
7 if ~ismember(flag, [0, 1])
8 flag = 0;
9 end
10
11 % iter_jacobi - Solve the system of linear equations of Ax = b using jacobi
12 % iteration method.
13 %
14 % Syntax: [x_iter, iter_times] = iter_jacobi(A, b, x_init, tol, iter_max)
15 %
16 % Jacobi iteration method:
17 % Let A be a square matrix, we decompose A as A = D - L - U, then we have
18 % the iterative scheme below:
19 % x_k = B x_k-1 + g,
20 % where B = D^-1 (L + U), g = D^-1 b.
21 %
22 % Input:
23 % A - Coefficient matrix.
24 % b - Column vector.
25 % x_init - Initial guess for the solution.
26 % tol - Tolerance for the stopping criterion.
27 % iter_max - Maximum number of iterations.
28 %
29 % Output:
30 % x_iter - Numerical solution approxiate to the true solution.
31 % iter_times - The times of iterations performed.
32
33 % Get the size of the matrix A and b, then check whether A is a square,
34 % and if the dimension of b matches A.
35 [m, n] = size(A);
36 assert(m == n, 'Matrix U must be square.');
37 assert(size(b, 1) == n, 'Dimension of b must match U.');
38
39 % Initialize Jacobi iterative matrix B, vector g and x_iter
40 B = zeros(n);
41 g = zeros(n, 1);
42 x_iter = x_init;
43
44 % Calculate the Jacobi iterative matrix B and the vector g
45 for i = 1:n
46
47 if A(i, i) == 0
48 error('Zero pivot encoutered.');
49 end
50
51 for j = i + 1:n
52 B(i, j) =- A(i, j) / A(i, i);
53 B(j, i) =- A(j, i) / A(i, i);
54 end
55
56 g(i) = b(i) / A(i, i);
57 end
58
59 q = norm(B);
60
61 if q >= 1
62 error('Jacobi iteration method does not converge.');
63 end
64
65 iEnd = n - flag;
66 % Perform iteration
67 for iter_times = 1:iter_max
68
69 x_old = x_iter;
70 x_iter = g;
71
72 for i = 1:iEnd
73
74 for j = i + 1:n
75 x_iter(i) = x_iter(i) + B(i, j) * x_old(j);
76 x_iter(j) = x_iter(j) + B(j, i) * x_old(i);
77 end
78
79 end
80
81 e = norm(x_iter - x_old);
82
83 if q / (1 - q) * e < tol
84 break;
85 end
86
87 end
88
89end
90
91function A = tridiag(N, v)
92 % tridiag - Generate a tridiagonal matrix.
93 %
94 % Syntax: A = tridiag(N, v)
95 %
96 % Input:
97 % N - dimension of the tridiagonal matrix.
98 % v - Tri-dimensional vector.
99 %
100 % Output:
101 % A - Tridiagonal matrix with the dimension of N.
102
103 A = zeros(N);
104
105 for i = 1:N - 1
106 A(i + 1, i) = v(1);
107 A(i, i) = v(2);
108 A(i, i + 1) = v(3);
109 end
110
111 A(N, N) = v(2);
112
113end
Data
如果不想运行,也可以直接下载结果,R2023b版本的Matlab。
- comparison-1.mat
- comparison-2.mat
- comparison-3.mat
- comparison-4.mat
- comparison-5.mat
- comparison-6.mat
- comparison-7.mat
- comparison-8.mat
- comparison-9.mat
- comparison-10.mat
- comparison-11.mat
- comparison-12.mat
- comparison-13.mat
- comparison-14.mat
- comparison-15.mat
- comparison-16.mat
- comparison-17.mat
- comparison-18.mat
- comparison-19.mat
- comparison-20.mat
文章标签
- 本站总访问量:loading次
- 本站总访客数:loading人
- 可通过邮件联系作者:Email大福
- 也可以访问技术博客:大福是小强
- 也可以在知乎搞抽象:知乎-大福
- Comments, requests, and/or opinions go to: Github Repository
