<-- Home
|--c
Kalman Filter by Gsl用C语言做一个速度跟踪的卡尔曼滤波器
系统模型
实现的卡尔曼滤波器用于跟踪一维空间中物体的位置和速度。系统动力学模型用线性系统来描述如下:
连续时间系统方程
$$ \dot{\mathbf{x}} = A_c \mathbf{x} + \mathbf{w} $$其中,状态向量 $\mathbf{x}$ 包含位置 $r$ 和速度 $v$,过程噪声 $\mathbf{w}$ 是均值为零的高斯白噪声,其强度矩阵为 $Q_c$。
观测过程可以表示为:
$$ z= H \mathbf{x} + \mathbf{v} $$其中,观测矩阵 $H$ 提取可测量的状态(位置),观测噪声 $\mathbf{v}$ 是均值为零的高斯白噪声,其协方差矩阵为 $R$。
离散时间系统方程
连续系统离散化后得到:
$$ \mathbf{x}_{k+1} = A\mathbf{x}_k + \mathbf{\nu}_k $$其中:
- $A = e^{A_c dt}$ 是离散状态转移矩阵
- $\mathbf{\nu}_k$ 是离散过程噪声,其协方差矩阵为 $Q$
- $dt$ 是采样时间间隔
状态向量
状态向量包含:
$$ \mathbf{x} = \begin{bmatrix} r \\\\ v \end{bmatrix} $$系统矩阵
连续时间系统矩阵:
$$ A_c = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} $$离散化后的状态转移矩阵:
$$ A = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & dt \\\\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} $$过程噪声协方差矩阵
连续时间过程噪声强度矩阵(假设加速度扰动):
$$ Q_c = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & q \end{bmatrix} $$其中 $q$ 是加速度噪声的强度(单位:$m^2/s^4$)。
离散化后的过程噪声协方差矩阵:
$$ Q = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{dt^4}{4}q & \frac{dt^3}{2}q \\\\ \frac{dt^3}{2}q & dt^2q \end{bmatrix} $$这在速度跟踪问题中的加速度噪声假设中的经典的结果,不在这里详细解释。
物理意义:
- $q$ 是连续时间加速度噪声强度(单位:$m^2/s^4$)
- 通过系统响应积分得到离散时间协方差矩阵
矩阵元素解释:
- $Q_{11}$:位置误差的方差,由加速度噪声经两次积分得到
- $Q_{22}$:速度误差的方差,由加速度噪声经一次积分得到
- $Q_{12}, Q_{21}$:位置和速度误差的协方差
测量模型
离散测量方程:
$$ z_k = H\mathbf{x}_k + \mathbf{v}_k $$测量矩阵:
$$ H = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} $$测量噪声协方差:
$$ R = [r] $$其中 $r$ 是位置测量噪声的方差(单位:$m^2$)
卡尔曼滤波器算法
该算法包含两个主要步骤:
预测步骤
状态预测:
$$ \hat{x}_{k|k-1} = A\hat{x}_{k-1|k-1} $$协方差预测:
$$ P_{k|k-1} = AP_{k-1|k-1}A^T + Q $$更新步骤
- 新息协方差:
- 卡尔曼增益:
- 状态更新:
- 协方差更新:
实现细节
矩阵运算
程序使用 GSL(GNU 科学库)进行矩阵运算:
gsl_blas_dgemm:矩阵乘法gsl_matrix_add:矩阵加法gsl_matrix_sub:矩阵减法gsl_matrix_scale:标量乘法
内存管理
实现过程中谨慎管理内存:
- 在初始化期间分配矩阵
- 使用临时矩阵进行中间计算
- 适时释放所有矩阵
仿真
主程序模拟:
- 匀速运动的真实轨迹
- 使用高斯噪声的带噪声测量
- 对这些测量进行滤波以估计真实状态
噪声参数
滤波器使用两个主要噪声参数:
- 过程噪声 ($\sigma_p^2 = 0.01$):模拟运动中的不确定性
- 测量噪声 ($\sigma_m^2 = 0.01$):模拟传感器的不确定性
性能
滤波器输出:
- 时间
- 真实位置
- 测量位置(带噪声)
- 估计位置
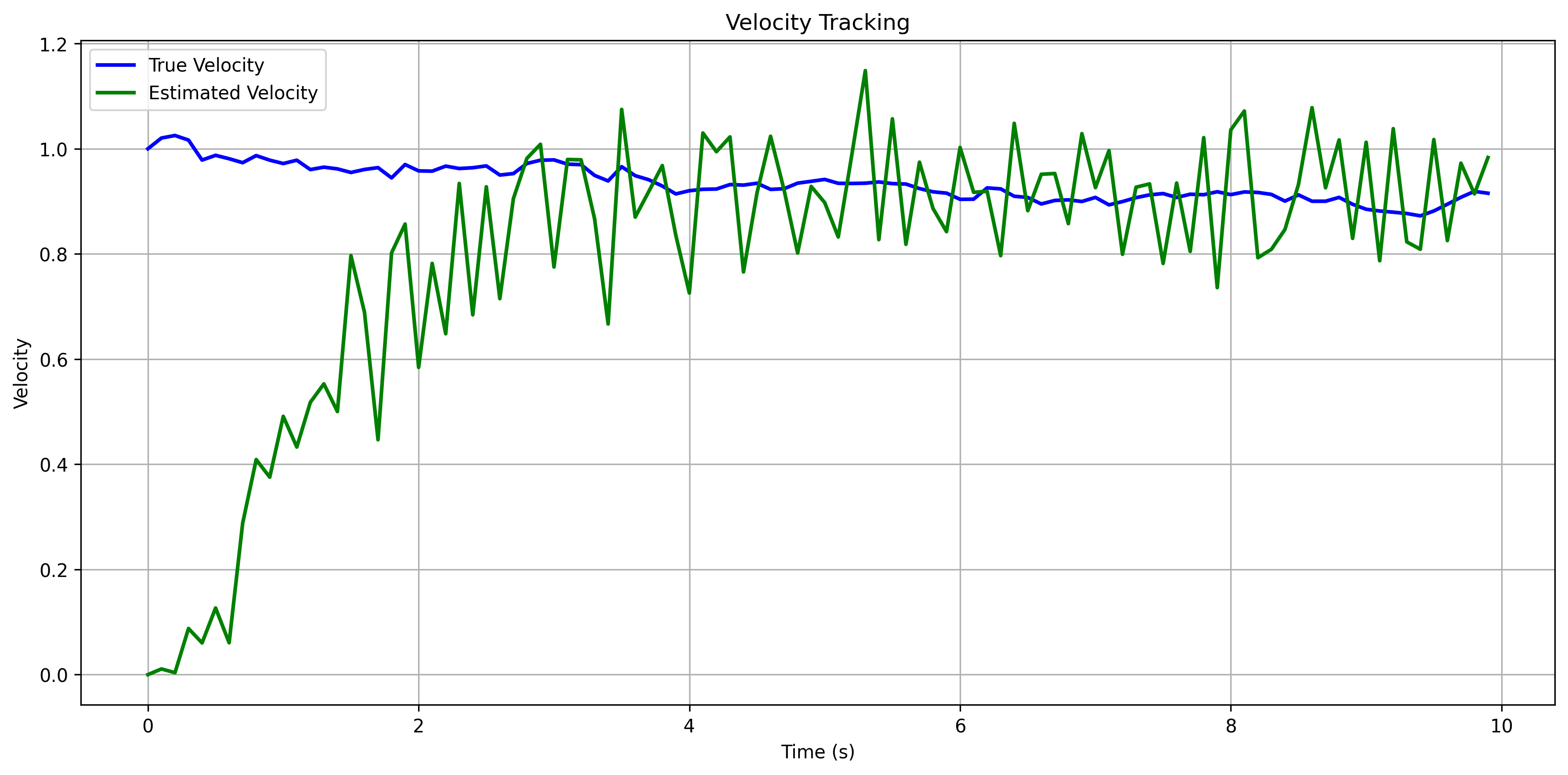
- 估计速度
随着处理更多的测量值,估计值应该收敛到真实值,滤波器能有效降低测量噪声同时跟踪真实状态。
代码实现与结果可视化
代码实现
1#include <stdio.h>
2#include <math.h>
3#include <gsl/gsl_matrix.h>
4#include <gsl/gsl_blas.h>
5#include <gsl/gsl_rng.h>
6#include <gsl/gsl_randist.h>
7
8// 卡尔曼滤波器结构体
9typedef struct
10{
11 gsl_matrix *A; // 状态转移矩阵
12 gsl_matrix *H; // 观测矩阵
13 gsl_matrix *Q; // 过程噪声协方差
14 gsl_matrix *R; // 测量噪声协方差
15 gsl_matrix *P; // 估计误差协方差
16 gsl_matrix *K; // 卡尔曼增益
17 gsl_matrix *x; // 状态向量 [位置, 速度]
18} KalmanFilter;
19
20// 初始化卡尔曼滤波器
21KalmanFilter *init_kalman_filter(double dt, double process_noise, double measurement_noise)
22{
23 KalmanFilter *kf = malloc(sizeof(KalmanFilter));
24
25 // 初始化矩阵
26 kf->A = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 2);
27 kf->H = gsl_matrix_alloc(1, 2);
28 kf->Q = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 2);
29 kf->R = gsl_matrix_alloc(1, 1);
30 kf->P = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 2);
31 kf->K = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 1);
32 kf->x = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 1);
33
34 // 设置状态转移矩阵 A
35 gsl_matrix_set(kf->A, 0, 0, 1.0);
36 gsl_matrix_set(kf->A, 0, 1, dt);
37 gsl_matrix_set(kf->A, 1, 0, 0.0);
38 gsl_matrix_set(kf->A, 1, 1, 1.0);
39
40 // 设置观测矩阵 H
41 gsl_matrix_set(kf->H, 0, 0, 1.0);
42 gsl_matrix_set(kf->H, 0, 1, 0.0);
43
44 // 设置过程噪声协方差 Q
45 gsl_matrix_set(kf->Q, 0, 0, 0.25 * dt * dt * dt * dt * process_noise);
46 gsl_matrix_set(kf->Q, 0, 1, 0.5 * dt * dt * dt * process_noise);
47 gsl_matrix_set(kf->Q, 1, 0, 0.5 * dt * dt * dt * process_noise);
48 gsl_matrix_set(kf->Q, 1, 1, dt * dt * process_noise);
49
50 // 设置测量噪声协方差 R
51 gsl_matrix_set(kf->R, 0, 0, measurement_noise);
52
53 // 初始化估计误差协方差 P
54 gsl_matrix_set_identity(kf->P);
55 gsl_matrix_scale(kf->P, 1.0);
56
57 // 初始化状态向量
58 gsl_matrix_set_zero(kf->x);
59
60 return kf;
61}
62
63// 预测步骤
64void predict(KalmanFilter *kf)
65{
66 // 临时矩阵
67 gsl_matrix *temp_2x2 = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 2);
68 gsl_matrix *temp_2x1 = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 1);
69
70 // x = A * x
71 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, 1.0, kf->A, kf->x, 0.0, temp_2x1);
72 gsl_matrix_memcpy(kf->x, temp_2x1);
73
74 // P = A * P * A' + Q
75 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasTrans, 1.0, kf->A, kf->P, 0.0, temp_2x2);
76 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, 1.0, temp_2x2, kf->A, 0.0, kf->P);
77 gsl_matrix_add(kf->P, kf->Q);
78
79 // 释放临时矩阵
80 gsl_matrix_free(temp_2x2);
81 gsl_matrix_free(temp_2x1);
82}
83
84// 更新步骤
85void update(KalmanFilter *kf, double measurement)
86{
87 // 临时矩阵
88 gsl_matrix *temp_1x2 = gsl_matrix_alloc(1, 2); // For H*P
89 gsl_matrix *temp_2x1 = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 1); // For P*H'
90 gsl_matrix *temp_1x1 = gsl_matrix_alloc(1, 1); // For H*x or innovation
91 gsl_matrix *S = gsl_matrix_alloc(1, 1); // Innovation covariance
92 gsl_matrix *z = gsl_matrix_alloc(1, 1); // Measurement
93 gsl_matrix *innovation = gsl_matrix_alloc(1, 1); // z - H*x
94
95 // 设置测量值
96 gsl_matrix_set(z, 0, 0, measurement);
97
98 // S = H * P * H' + R
99 // First compute H*P (1x2 * 2x2 = 1x2)
100 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, 1.0, kf->H, kf->P, 0.0, temp_1x2);
101 // Then (H*P) * H' (1x2 * 2x1 = 1x1)
102 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasTrans, 1.0, temp_1x2, kf->H, 0.0, S);
103 gsl_matrix_add(S, kf->R);
104
105 // K = P * H' * S^(-1)
106 // First compute P*H' (2x2 * 2x1 = 2x1)
107 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasTrans, 1.0, kf->P, kf->H, 0.0, temp_2x1);
108 // Then scale by S^(-1)
109 double s_inv = 1.0 / gsl_matrix_get(S, 0, 0);
110 gsl_matrix_memcpy(kf->K, temp_2x1);
111 gsl_matrix_scale(kf->K, s_inv);
112
113 // 计算创新项 (innovation = z - H*x)
114 // First compute H*x (1x2 * 2x1 = 1x1)
115 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, 1.0, kf->H, kf->x, 0.0, temp_1x1);
116 gsl_matrix_memcpy(innovation, z);
117 gsl_matrix_sub(innovation, temp_1x1);
118
119 // x = x + K * innovation
120 // K*innovation (2x1 * 1x1 = 2x1)
121 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, 1.0, kf->K, innovation, 1.0, kf->x);
122
123 // P = (I - K*H) * P
124 // First compute K*H (2x1 * 1x2 = 2x2)
125 gsl_matrix *temp_2x2 = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 2);
126 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, -1.0, kf->K, kf->H, 0.0, temp_2x2);
127 gsl_matrix_set_identity(temp_2x2); // Add identity matrix
128 // Then multiply by P
129 gsl_matrix *new_P = gsl_matrix_alloc(2, 2);
130 gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, 1.0, temp_2x2, kf->P, 0.0, new_P);
131 gsl_matrix_memcpy(kf->P, new_P);
132
133 // 释放临时矩阵
134 gsl_matrix_free(temp_1x2);
135 gsl_matrix_free(temp_2x1);
136 gsl_matrix_free(temp_1x1);
137 gsl_matrix_free(temp_2x2);
138 gsl_matrix_free(new_P);
139 gsl_matrix_free(S);
140 gsl_matrix_free(z);
141 gsl_matrix_free(innovation);
142}
143
144// 释放卡尔曼滤波器
145void free_kalman_filter(KalmanFilter *kf)
146{
147 gsl_matrix_free(kf->A);
148 gsl_matrix_free(kf->H);
149 gsl_matrix_free(kf->Q);
150 gsl_matrix_free(kf->R);
151 gsl_matrix_free(kf->P);
152 gsl_matrix_free(kf->K);
153 gsl_matrix_free(kf->x);
154 free(kf);
155}
156
157int main()
158{
159 // 初始化随机数生成器
160 gsl_rng *rng = gsl_rng_alloc(gsl_rng_default);
161 gsl_rng_set(rng, 1234);
162
163 // 初始化卡尔曼滤波器参数
164 double dt = 0.1; // 时间步长
165 double process_noise = 0.01; // 过程噪声
166 double measurement_noise = 0.01; // 测量噪声
167
168 // 创建卡尔曼滤波器
169 KalmanFilter *kf = init_kalman_filter(dt, process_noise, measurement_noise);
170
171 // 模拟数据
172 double true_position = 0.0;
173 double true_velocity = 1.0;
174
175 // 使用固定宽度格式化输出表头
176 printf("#%8s\t%8s\t%8s\t%8s\t%8s\t%8s\n",
177 "Time", "True Pos", "True Vel",
178 "Meas Pos",
179 "Est Pos", "Est Vel");
180
181 // 运行模拟
182 for (int t = 0; t < 100; t++)
183 {
184 // 加速度扰动考虑
185 true_velocity += gsl_ran_gaussian(rng, sqrt(process_noise)) * dt;
186
187 // 更新真实状态
188 true_position += true_velocity * dt;
189
190 // 生成带噪声的测量值
191 double measurement = true_position + gsl_ran_gaussian(rng, sqrt(measurement_noise));
192
193 // 卡尔曼滤波
194 predict(kf);
195 update(kf, measurement);
196
197 // 使用固定宽度格式化输出数据
198 printf("%9.2f\t%8.4f\t%8.4f\t%8.4f\t%8.4f\t%8.4f\n",
199 t * dt,
200 true_position,
201 true_velocity,
202 measurement,
203 gsl_matrix_get(kf->x, 0, 0),
204 gsl_matrix_get(kf->x, 1, 0));
205 }
206
207 // 清理
208 free_kalman_filter(kf);
209 gsl_rng_free(rng);
210
211 return 0;
212}
编译:
1gcc kalman.c -o kalman -lgsl -lgslcblas -lm
需要系统中安装了 gsl 库。安装方法:
1sudo apt-get install libgsl-dev
运行:
1./kalman > kalman_data.txt
就能看到一个文本文件 kalman_data.txt,里面记录了时间、真实位置、真实速度、测量位置、估计位置、估计速度。
结果可视化
很无聊的用Python做了一个可视化,直接从c代码生成可执行文件,然后捕获输出画图。
1import subprocess
2import numpy as np
3import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
4import os
5
6
7def compile_kalman():
8 """Compile the Kalman filter C program"""
9 try:
10 result = subprocess.run(
11 ['gcc', 'kalman.c', '-o', 'kalman', '-lgsl', '-lgslcblas', '-lm'],
12 capture_output=True,
13 text=True
14 )
15 if result.returncode != 0:
16 print("Error compiling kalman filter:")
17 print(result.stderr)
18 return False
19 return True
20 except Exception as e:
21 print(f"Error during compilation: {e}")
22 return False
23
24
25def run_kalman_filter():
26 """Run the Kalman filter executable and return the results"""
27 try:
28 # First compile the program
29 if not compile_kalman():
30 return None
31
32 # Run the executable and capture output
33 result = subprocess.run(['./kalman'], capture_output=True, text=True)
34
35 # Clean up the executable
36 try:
37 os.remove('./kalman')
38 except OSError as e:
39 print(f"Warning: Could not remove executable: {e}")
40
41 if result.returncode != 0:
42 print("Error running kalman filter executable")
43 return None
44
45 # Parse the output
46 lines = result.stdout.strip().split('\n')
47
48 # Skip the header line (starts with #)
49 data = np.array([line.split()
50 for line in lines if not line.startswith('#')], dtype=float)
51
52 return data
53 except Exception as e:
54 print(f"Error: {e}")
55 # Try to clean up if something went wrong
56 try:
57 os.remove('./kalman')
58 except OSError:
59 pass
60 return None
61
62
63def plot_position(data):
64 """Plot position tracking results"""
65 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
66
67 time = data[:, 0]
68 plt.plot(time, data[:, 1], 'b-', label='True Position', linewidth=2)
69 plt.scatter(time, data[:, 3], c='r', s=20, alpha=0.5, label='Measurements')
70 plt.plot(time, data[:, 4], 'g-', label='Estimated Position', linewidth=2)
71
72 plt.title('Position Tracking')
73 plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
74 plt.ylabel('Position')
75 plt.grid(True)
76 plt.legend()
77
78 plt.tight_layout()
79 plt.savefig('kalman_filter_position.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
80 plt.close()
81
82
83def plot_velocity(data):
84 """Plot velocity tracking results"""
85 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
86
87 time = data[:, 0]
88 plt.plot(time, data[:, 2], 'b-', label='True Velocity', linewidth=2)
89 plt.plot(time, data[:, 5], 'g-', label='Estimated Velocity', linewidth=2)
90
91 plt.title('Velocity Tracking')
92 plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
93 plt.ylabel('Velocity')
94 plt.grid(True)
95 plt.legend()
96
97 plt.tight_layout()
98 plt.savefig('kalman_filter_velocity.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
99 plt.close()
100
101
102def plot_results(data):
103 """Plot all results"""
104 plot_position(data)
105 plot_velocity(data)
106
107 # Create a combined plot for display
108 fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(12, 10))
109 fig.suptitle('Kalman Filter Results', fontsize=16)
110
111 # Get time array
112 time = data[:, 0]
113
114 # Plot position tracking
115 ax1.plot(time, data[:, 1], 'b-', label='True Position', linewidth=2)
116 ax1.scatter(time, data[:, 3], c='r', s=20, alpha=0.5, label='Measurements')
117 ax1.plot(time, data[:, 4], 'g-', label='Estimated Position', linewidth=2)
118
119 ax1.set_title('Position Tracking')
120 ax1.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
121 ax1.set_ylabel('Position')
122 ax1.grid(True)
123 ax1.legend()
124
125 # Plot velocity tracking
126 ax2.plot(time, data[:, 2], 'b-', label='True Velocity', linewidth=2)
127 ax2.plot(time, data[:, 5], 'g-', label='Estimated Velocity', linewidth=2)
128
129 ax2.set_title('Velocity Tracking')
130 ax2.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
131 ax2.set_ylabel('Velocity')
132 ax2.grid(True)
133 ax2.legend()
134
135 # Adjust layout and display
136 plt.tight_layout()
137 plt.show()
138
139
140def main():
141 # Run Kalman filter and get data
142 data = run_kalman_filter()
143 if data is not None:
144 # Plot results
145 plot_results(data)
146 else:
147 print("Failed to get data from Kalman filter")
148
149
150if __name__ == "__main__":
151 main()
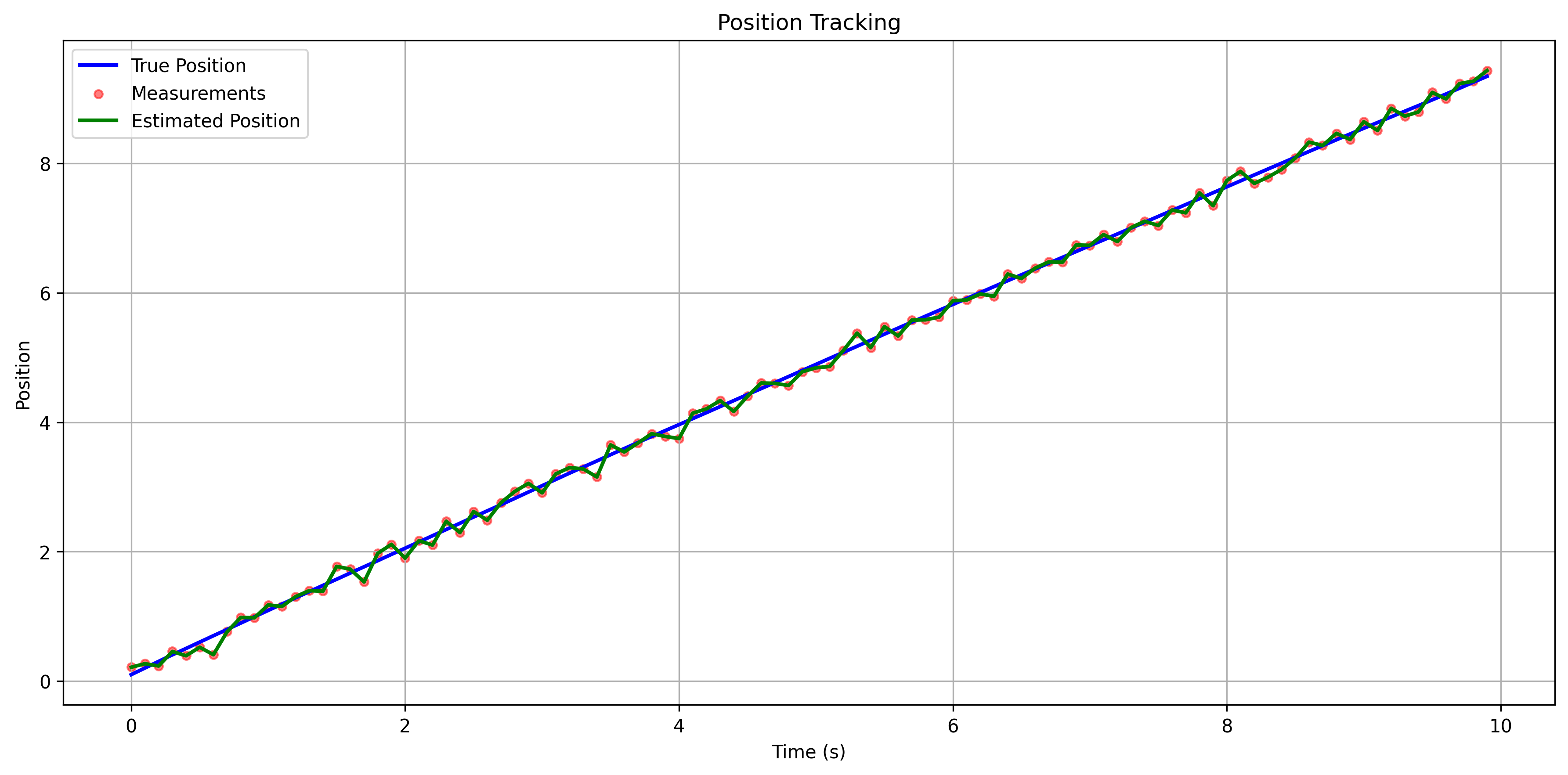
可以看到,我们从速度0开始,很快就追踪到速度1附近,然后速度估计基本就稳定在1附近了。
文章标签
|-->c |-->kalman filter |-->gsl
- 本站总访问量:loading次
- 本站总访客数:loading人
- 可通过邮件联系作者:Email大福
- 也可以访问技术博客:大福是小强
- 也可以在知乎搞抽象:知乎-大福
- Comments, requests, and/or opinions go to: Github Repository
